Category: Truck News & Info
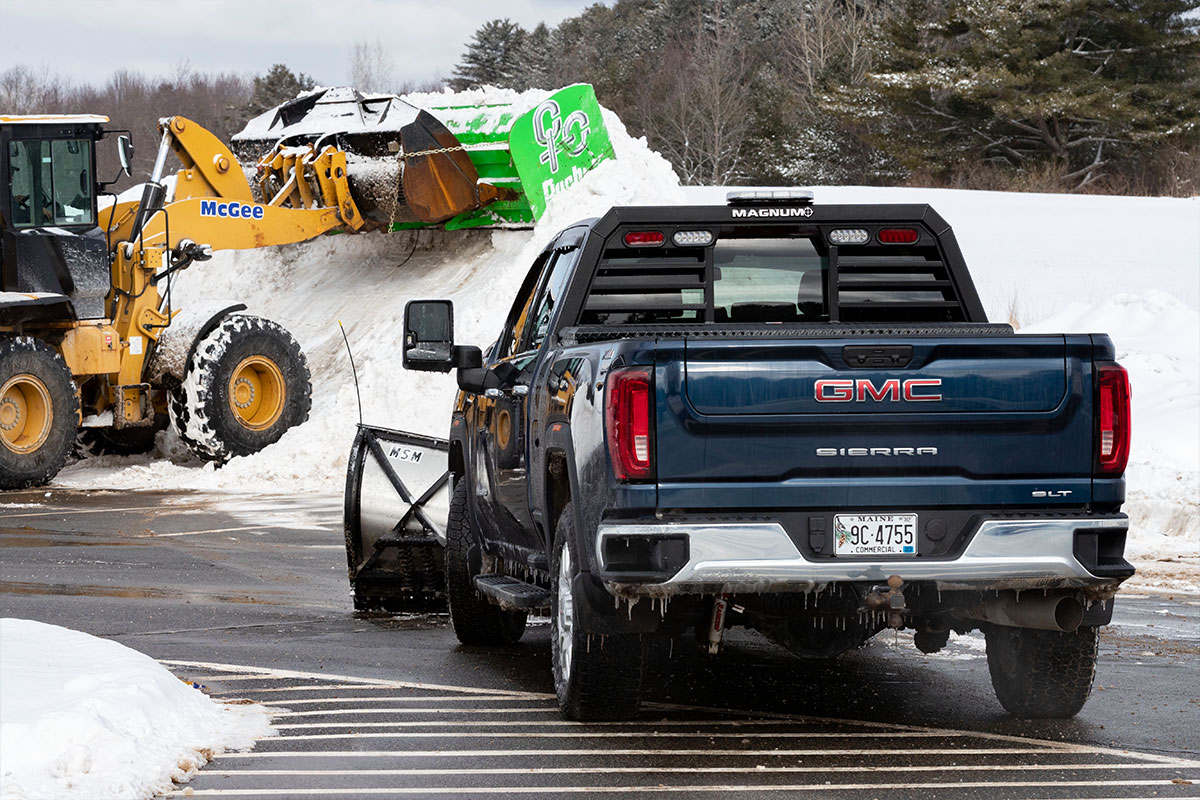
Getting your pickup truck ready for snow plowing season is a great project to tackle before the snow starts falling. Be ready before the temperatures plummet, and you’ll never lose response time when Mother Nature starts storming!
Magnum’s headache racks, LED lights, and other accessories are a great addition to your snow plowing setup. Let’s look at some other essential snow plowing accessories to make your snow plow plans complete.
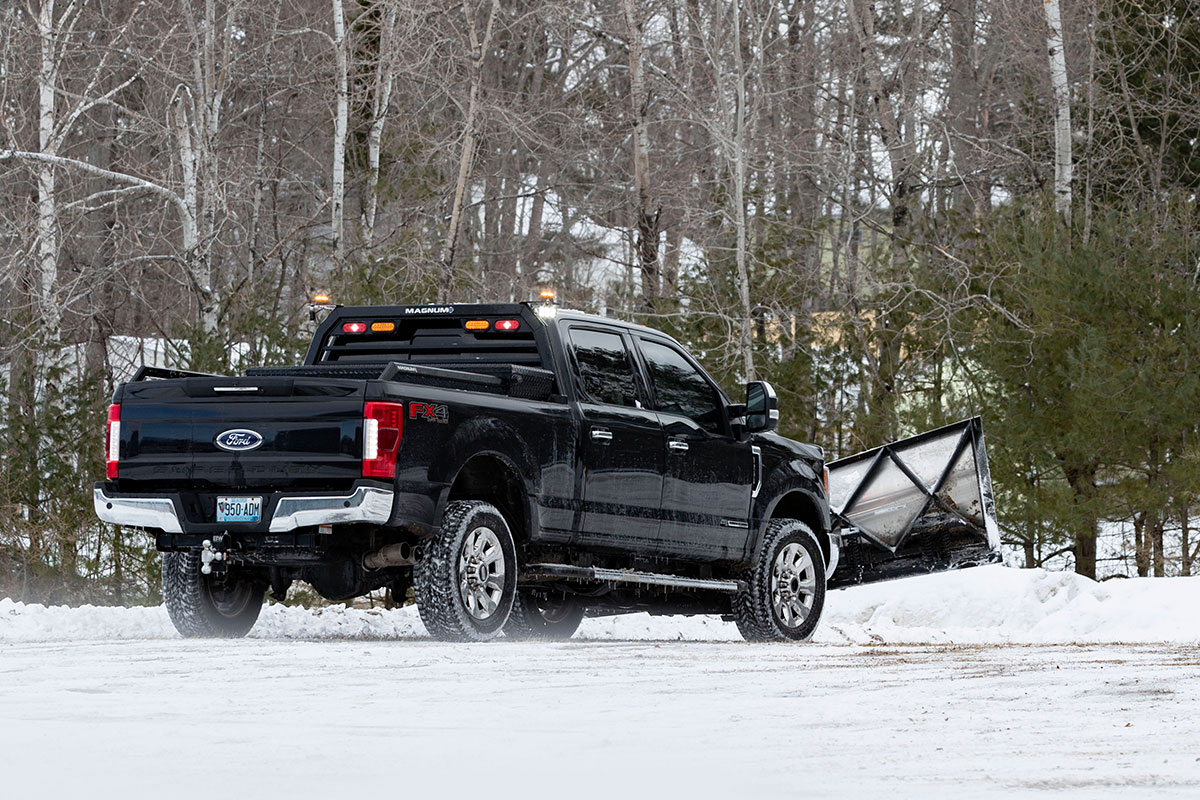


If You Need a Snow Plow
If you don’t already have a snow plow installed on your truck, start there. Key considerations when choosing a plow include the weight and width of the plow; the style of blade and control you prefer; and of course, your budget.
The smaller your truck and the lower its GVWR, the narrower, lighter plow you need to purchase. For example, if you drive a Toyota Tacoma, you’ll be looking for a smaller plow than if you drive a Ford F-350, but both trucks can be outfitted for snow removal.
Snow plows come in a variety of styles, including straight blade and V-blade, with different types of hydraulic control options. Materials including steel – the long-standing industry standard – and polyethylene blades are available.
Your best bet for getting the best plow for your truck is to work with a local dealer! Once your plow is selected and installed, it’s time to accessorize.
Magnum Accessories For Snow Plow Success
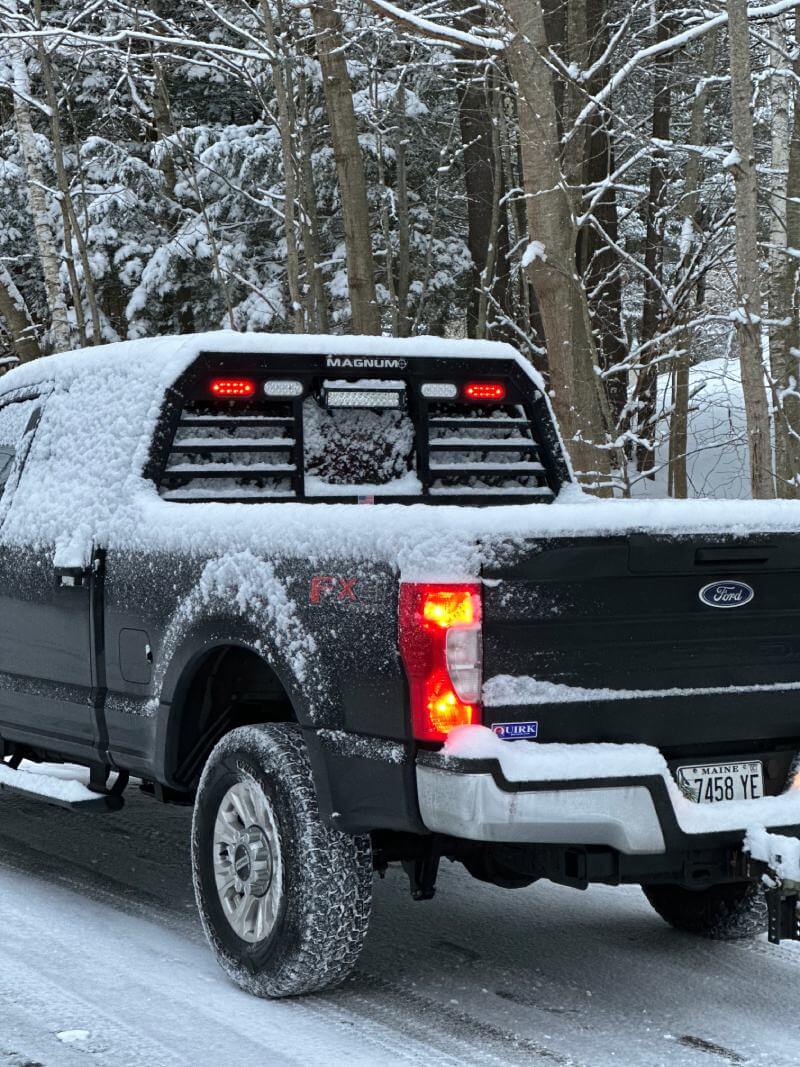
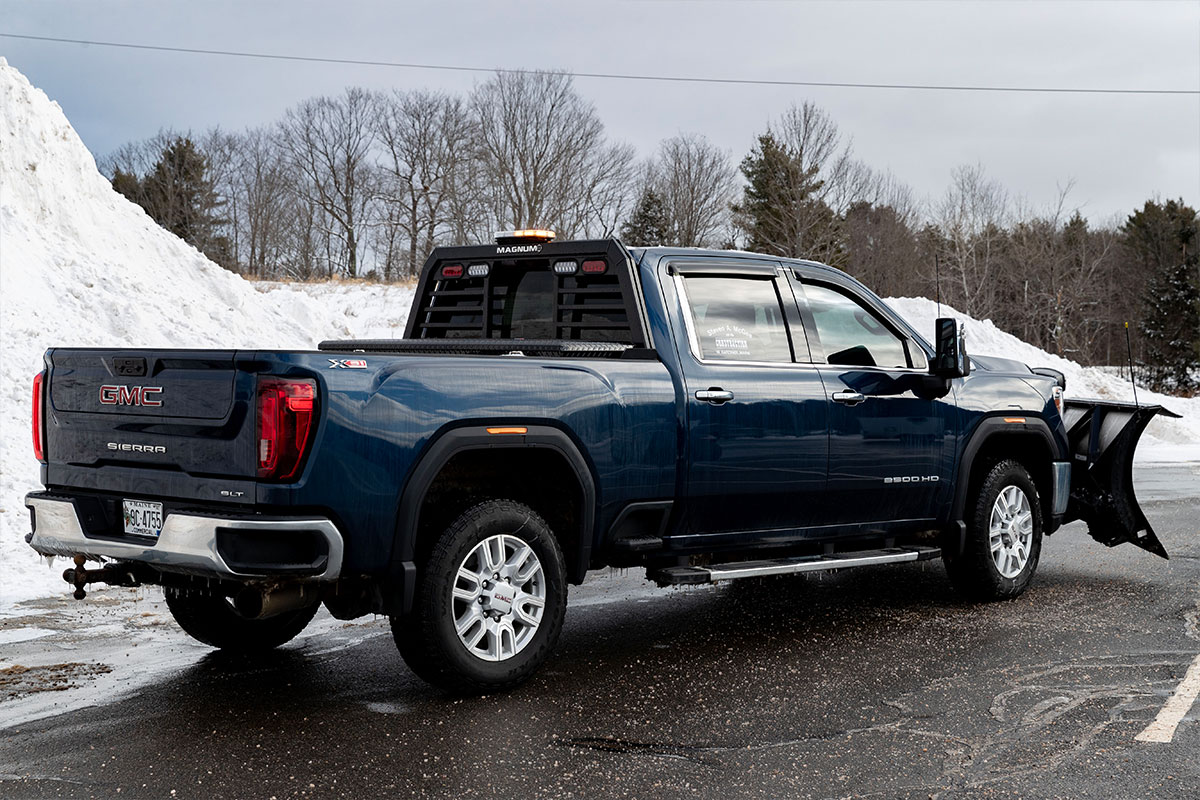
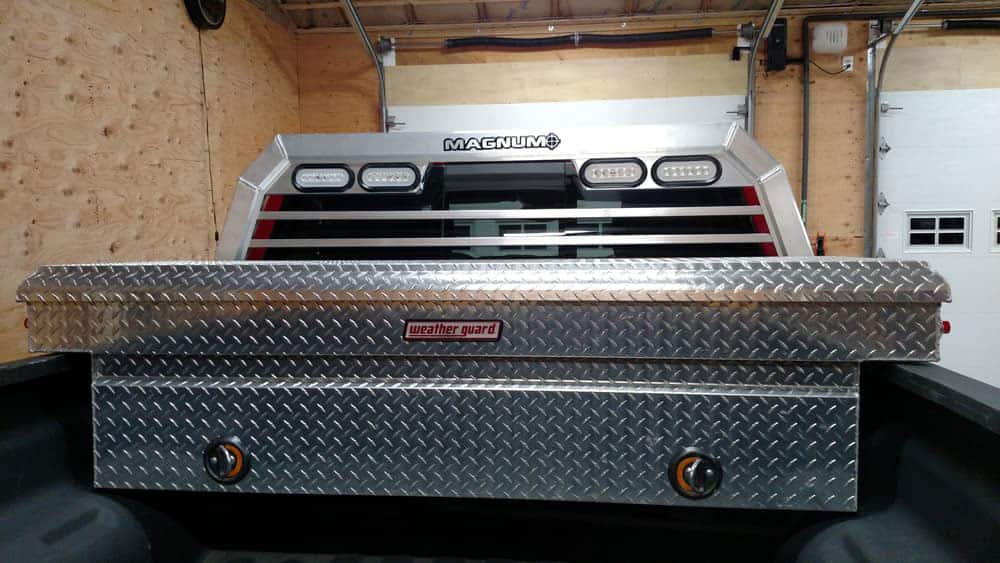
While you’re setting up your truck for winter’s most important task, don’t forget to get the pickup truck bed ready, too. If you don’t already have a Magnum headache rack, now is the time to order one.
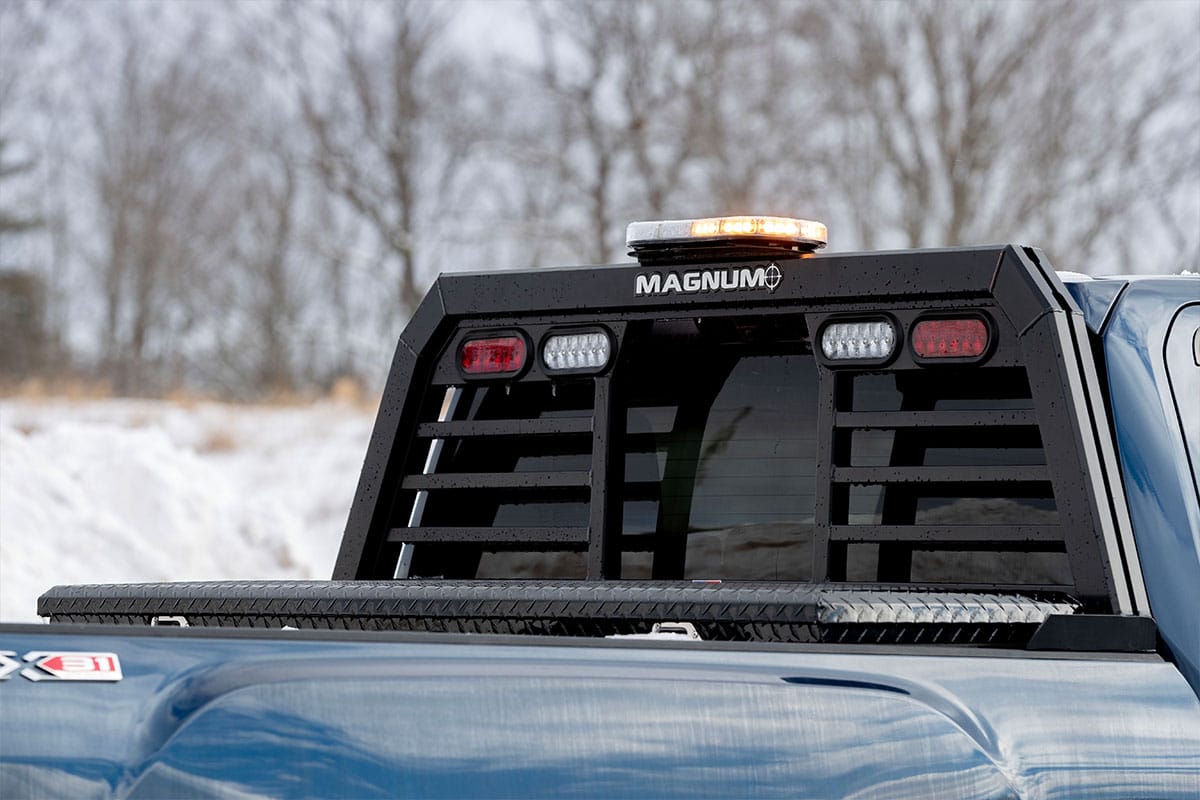


A lighted headache rack with Glide Track D-rings and cargo stops is a great addition to your snow plow setup. Keeping a shovel or other tools in the truck bed? Secure them to the headache rack for easy access and secure transport. A headache rack protects your rear window year-round and always gives you extra cargo options.
Extra light brackets and LED lights for your Magnum truck rack let you shed some extra light on manual snow removal jobs like shoveling or spreading sand. And because your Magnum truck rack is built to fit your truck, including your tonneau cover, it seamlessly integrates into your winter setup.
A Magnum Rack Pack is a great way to get all the Magnum essentials you want in one easy order. Choose your headache rack, and get truck bed rails, a rear cargo rack and extension tube. You could also choose a Commander Lighting Package (add during checkout) to really get the most for your money and be ready to light up the darkest nights this winter.
Extras For Your Truck and Plow
Once you have a plow and Magnum rack installed on your truck, what other upgrades do you want?
If your truck doesn’t already have a backup camera, it’s a worthwhile upgrade to consider if you do a lot of snow plowing. Snow plow-specific models are available, including heated lenses, so you never miss a thing even in the worst weather conditions.
Using ballast, such as bags of sand or salt, in your pickup truck bed to help offset the weight of the snow plow? A ballast retainer keeps your load secured and evenly distributed.
Add-ons for the plow itself can optimize your operation. Plow guides are a low-tech visibility option for the ends of the plow blades for in-cab visibility. Plow wings and snow deflectors can up your plow game by expanding your plow blade’s reach and keeping snow out of your line of sight.
Plow shoes attach to the bottom of a snow plow’s blade, which is useful for preventing plow damage to soft surfaces like grass or dirt. Consider these handy accessories if you’ve ever accidentally plowed up a section of the lawn!
Finally, consider dolly wheels for your plow blade if you need the option to move your plow blade during the off-season. While the plow blade is stored, you can easily relocate it inside the garage, shop, or on the driveway without dragging the blade or throwing out your back trying to lift it.
Other Essentials to Keep in Your Truck
Don’t forget to keep some basic essentials handy in your truck any time you head out in the snow, whether you’re plowing or not.
We recommend some basics, like an extra pair of warm gloves, a hat, a blanket, and a water bottle. A first aid kit, extra cell phone charger, and a flashlight or headlamp are must-haves. Don’t forget the snow and ice scraper and a pair of jumper cables.
You might also want to throw tire chains and a tow strap in the truck bed – just in case!
For All Seasons and All Weather
Magnum truck racks are designed to perform in all seasons, all weather, and for any pickup truck. Even when the snow plowing season ends for another year, you’ll be glad you invested in the right gear and a year-round Magnum headache rack.
Whatever truck rack accessories you need – from tool box leveling spacers to sliding D-rings and cargo stops or even truck bed rails and an integrated cargo rack, Magnum has the accessories you’re looking for.
Get installation guides and check out what other happy Magnum customers are saying – then order your rack today!
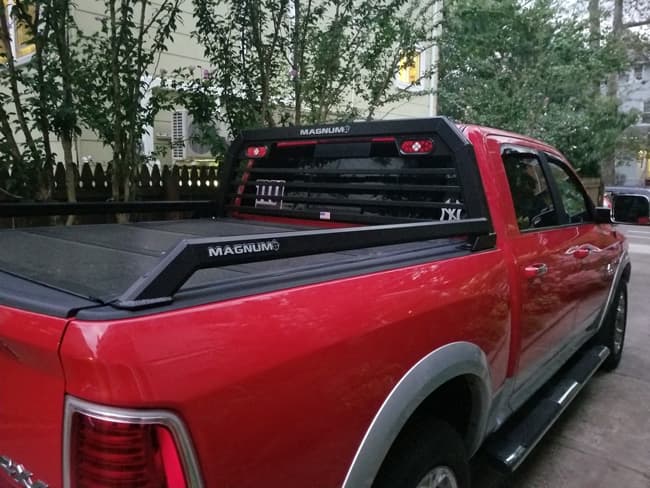
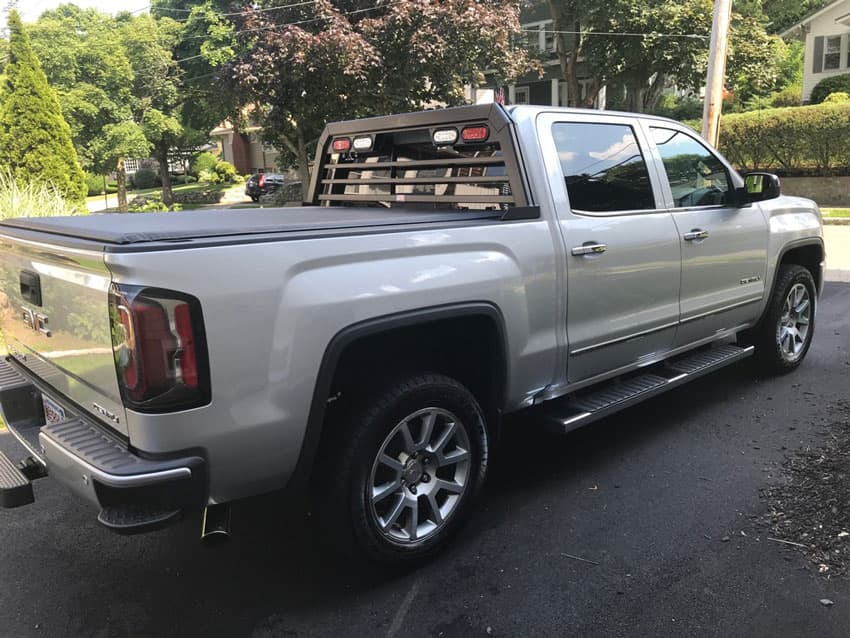
When setting up your truck bed, there are a few essentials you can’t skip. Two of our favorites are the hard-working duo of a truck rack and a truck bed cover or tonneau cover.
Protect your truck window and secure cargo easily with a Magnum rack and accessories, and keep items hidden and secured in the bed with a truck bed cover – also called a tonneau cover. Even when your truck bed is empty, a tonneau cover protects it from debris and the elements. Plus, it looks great – especially paired with a Magnum rack.


The key to using this pair of accessories to their full advantage is getting a truck rack and tonneau cover that fit together correctly and install securely, so before you buy, check out Magnum’s guide to pairing your truck rack and truck bed cover for best results. As always, the key to success is in the details – the right fit makes all the difference!
Have a Tonneau Cover and Need a Magnum Truck Rack?
For truck owners who already have a tonneau cover and want to add a Magnum headache rack to their setup, Magnum makes it easy.
When you order a Magnum truck rack, we ask about your truck – the make, model, and year, plus whether you have a tonneau cover. If you do, then indicate whether your tonneau cover sits above or between the rails, and verify with Magnum’s photo guide that you have the correct selection. Then, finish your order and Magnum will build your truck rack!
When it arrives – check out our convenient installation guides to get your Magnum headache rack installed with your tonneau cover for an instant upgrade.
Have a Magnum Rack and Need a Tonneau Cover?
Here’s where some research might save you costly trial and error. Look at where your Magnum rack is mounted. Now, when you look for a truck bed cover, search for options that won’t clash with your truck rack installation.
This probably means you want to look for a between-the-rails truck bed tonneau cover. You may also want to avoid hinged or folding styles if their range of motion is going to interfere with your Magnum rack. Check out retractable or roll-up tonneau covers; the good news is, with so many options on the market you are sure to find the truck bed cover you need.
What’s this going to cost? You can spend a serious stack of cash on a truck bed cover – think a few thousand dollars. But if that’s not your budget, don’t worry. More affordable options start around $200. Generally, a roll-up style cover is going to be the most affordable.
Starting From Scratch?
If you need a truck rack and tonneau cover, we suggest deciding on your tonneau cover first and then customizing your Magnum rack accordingly. Also consider adding extras like truck bed rails, rear cargo racks, or a Commander Lighting Package at the same time so you don’t have to do extra work down the road!
Magnum also offers a cargo rack extension tube and a range of accessories including D-rings and cargo stops, LED lights, wiring harnesses, and light brackets. We even offer leveling spacers to make sure your truck toolbox is a perfect fit with your Magnum rack.
Even More From Magnum
Learn more about what Magnum can do for you, with a rugged, reliable, American-made truck rack and all the accessories you need. When you choose Magnum’s design and craftsmanship, you can’t go wrong! Add a truck bed cover and a Magnum headache rack to your truck for the ultimate accessory upgrade. Trust our installation guides to help you get back on the road looking better than ever.
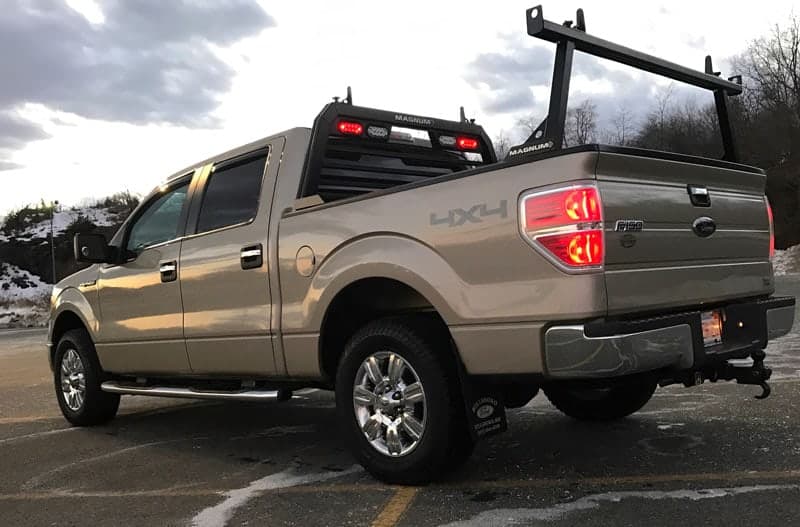
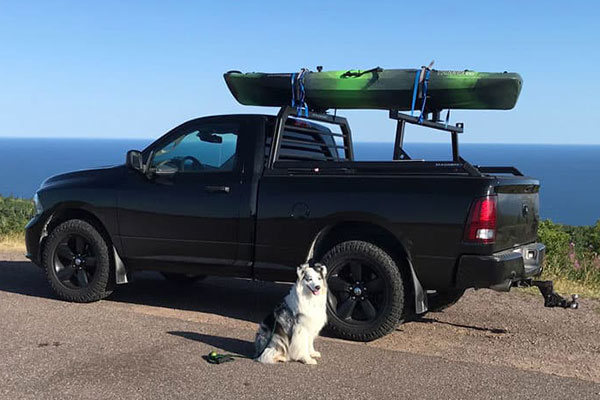
Magnum builds more than just headache racks for your pickup truck. A rear cargo rack is the perfect addition to help get longer cargo from here to there. Fortunately, Magnum builds rear racks that seamlessly integrate with both our headache racks and our truck bed rails.
Few things shine brighter than LED light. Find these energy-efficient, ultra-bright bulbs everywhere from a string of holiday lights, to headlamps, to after-market light bars for your truck.
Once your truck is decked out with a Magnum headache rack, rear cargo rack, and truck bed rails, don’t forget to look at our LED light bars and mounting hardware. They’re designed to work with the Glide Track system on your truck rack for maximum convenience.
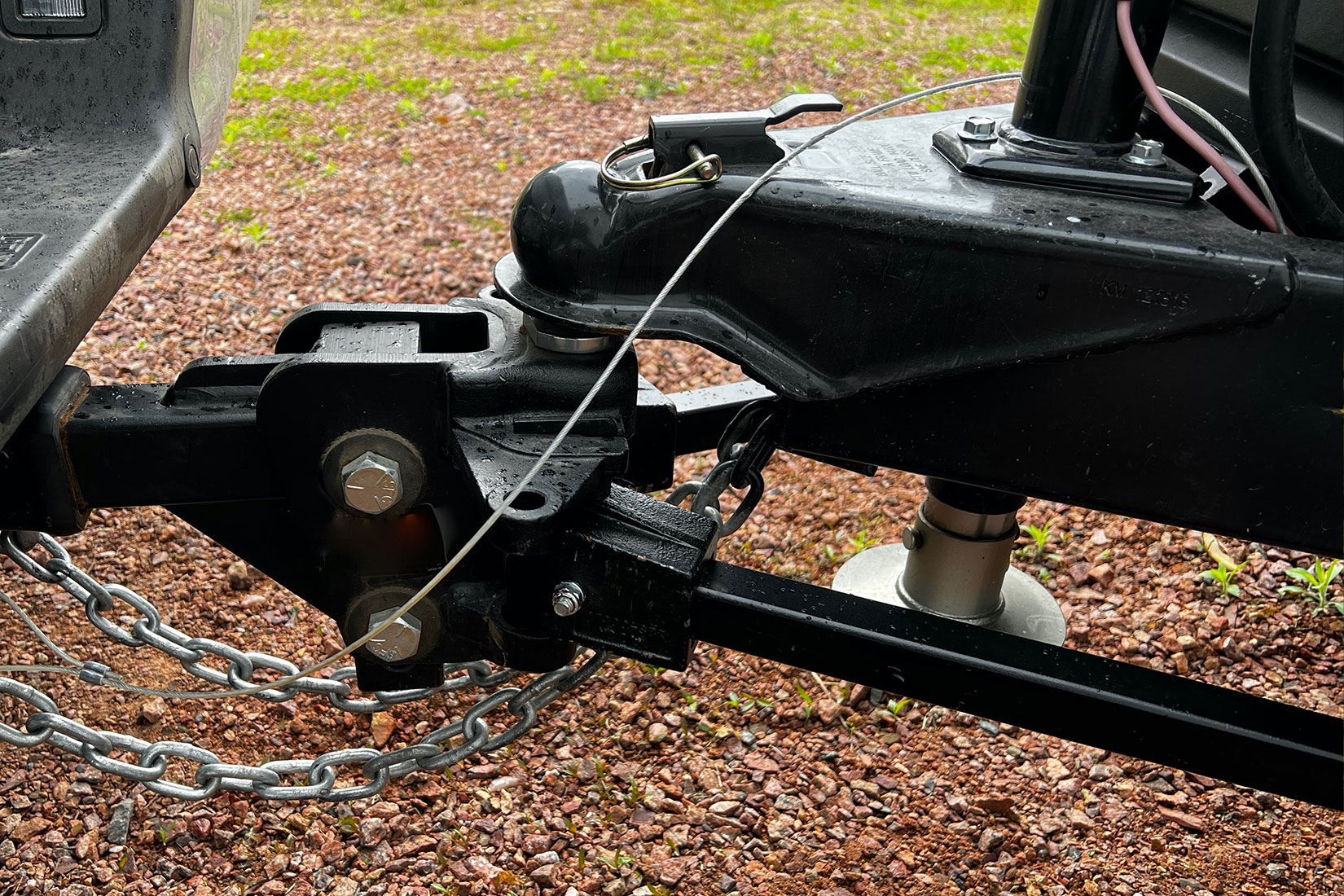
Need to tow something? It’s the best way to move stuff from here to there, and it’s simple in theory. But the reality of hitching a trailer to your truck requires you to have the right pieces working together for a safe, successful haul.
If you need a great tow setup and aren’t sure where to start, let’s look at the different types of trailer hitches available and what might lead you to choose one over another. Remember that this guide is meant to offer general information, but can’t capture the detail of every vehicle, tow hitch, and trailer combination out there.
It’s important to consult with your local trailer rep or dealership to make sure that you choose the right products for your vehicle’s GVWR, the trailer you intend to haul, the cargo it’s carrying, and any other specs you need to know. Let’s look at the different types of tow hitches available so you have a better idea of where to get started.
After a Magnum truck rack, one of the best accessories you can choose for your truck is a tool box. Haul and protect frequently used tools or gear in a secure, organized space that guards against the elements.
Our Magnum customers tell us they love the combination of a headache rack and a truck toolbox. Secured tools, an American-made truck rack, and cargo tie-downs for gear – it’s the perfect combination for your truck.
Whether you already own a tool box and want to add a truck rack – or vice versa – the key is getting the right fit for your truck.
Magnum builds some of the best truck racks on the road. We proudly design and build our headache racks in the USA – in Maine. With Magnum’s extensive options, you can get the exact look and fit you want for your pickup truck.
Magnum products are designed to look great and level up your truck’s style. Most important, they help you get more done with your truck, while protecting your windows, cargo, and passengers. All welded aluminum construction with powder coated finish provides exceptional durability and lightweight performance.
Whether you’re a weekend warrior configuring a plow truck with light bars and strobes, a carpenter hauling lumber to the jobsite, or an angler hauling the canoe to the next pond, a Magnum truck rack is a must-have part of your setup. Secured to the stake pockets built into your truck bed, Magnum headache racks are easy to install. With Magnum accessories like truck bed rails and rear cargo racks, turn up your truck’s hauling game and add custom light and tie-down options.
Owning a truck means more than just having a great way to get around. A truck is the modern-day workhorse, always ready to haul your gear and transport your family. Fortunately, there are a wealth of accessories on the market to really make the most of your investment.
Accessories like LED light bars, trailer hitches, and Magnum headache racks let you do more with your pickup. With parts and information readily available, you can even perform some of these upgrades yourself. Depending on your level of expertise, or your comfort with learning on the job, do-it-yourself truck upgrades can be a fun and budget-friendly way to kit out your pickup.
If you’re a gun owner, then you know that where you store your guns and ammo is one of the most important parts of gun ownership. But have you considered the wide variety of firearm accessories for your truck? There are a whole load of them available. But which ones do you need for your truck? From console safes to under-dash holsters, we’ve rounded up the best tactical firearm pickup truck accessories of 2021.
DECKED Truck Bed Storage Drawers
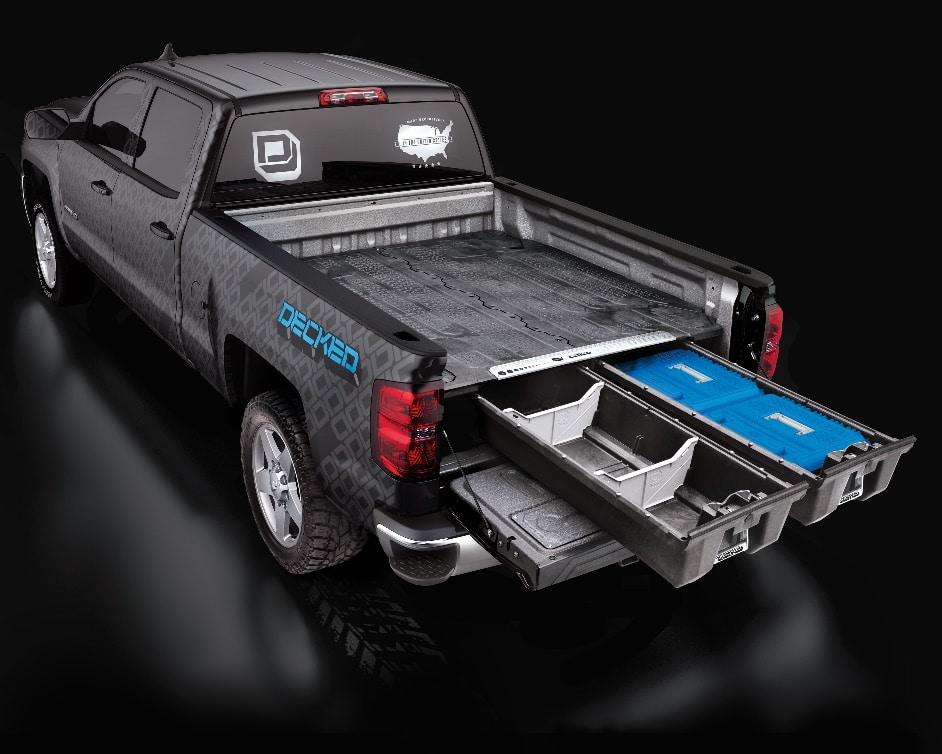

Once installed, it’s hardly noticeable. You also retain full use of your truck bed since the DECKED truck bed storage drawers can withstand up to 2000-pound payload in your bed. Each drawer can hold up to 200 pounds of gear, so you won’t need to worry about overloading it. It’s weatherproof, durable, secure, and easily installed without drilling for most vehicles.
Great Day Center-Lok Overhead Gun Rack
Prefer to keep your guns where you can see them? An easily accessible overhead gun rack might be your thing. This universal overhead gun rack fits a variety of truck models, SUVs, and even a few sedans. The padded holster arms and sturdy Velcro straps keep your guns in place while you’re rambling around in your truck.
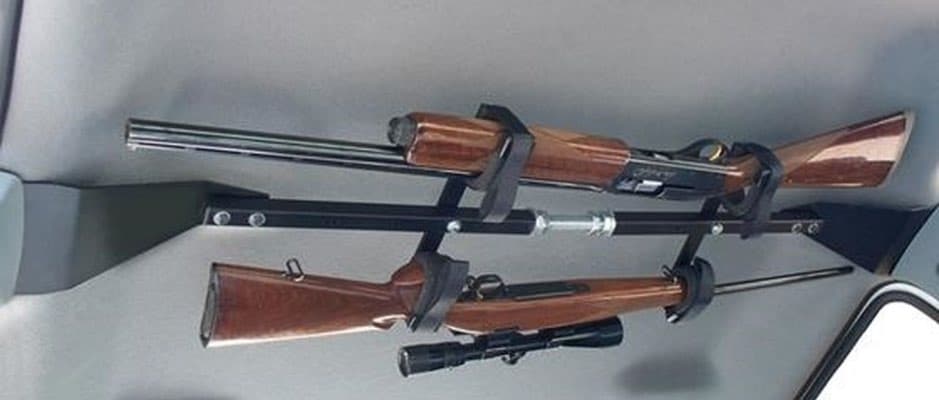

It’s customizable with either one or two-gun configurations. Installation does require some elbow grease, but it’s not an impossible DIY. It arrives in two pieces, so you’ll need to slide the two pieces together first. To install it in your truck, no drilling or bolting is required. All you need to do is slide the end pieces under the plastic b-pillar trim in your cab and you’re all set.
RAPiD® Console Safe
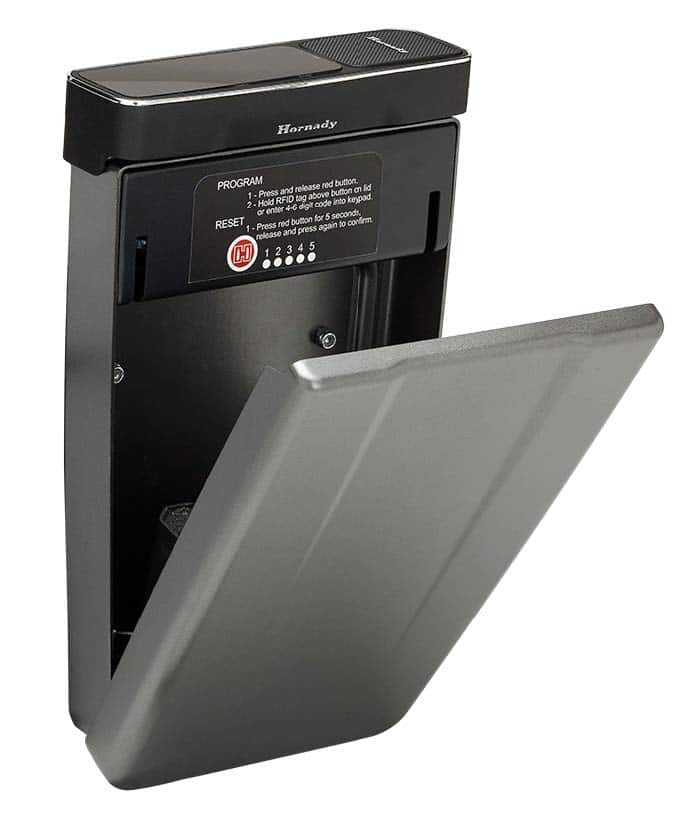

This bad boy has an exterior housing made of heavy-duty, tamper-proof 14-gauge steel. It installs with an inflatable bladder, which means you won’t have to do any destructive modification to install it. Once it’s in place, it also comes with a security cable so you can attach it to your seat frame. The best part? It’s got both RFID and barrel key locking options. It comes with an RFID wristband, RFID key fob and two RFID stickers for quick access when you need it most. This convenience is what puts the RAPiD® console safe on the list of the best tactical firearm pickup truck accessories of 2021.
SEATVAULT® Cab Storage Vault
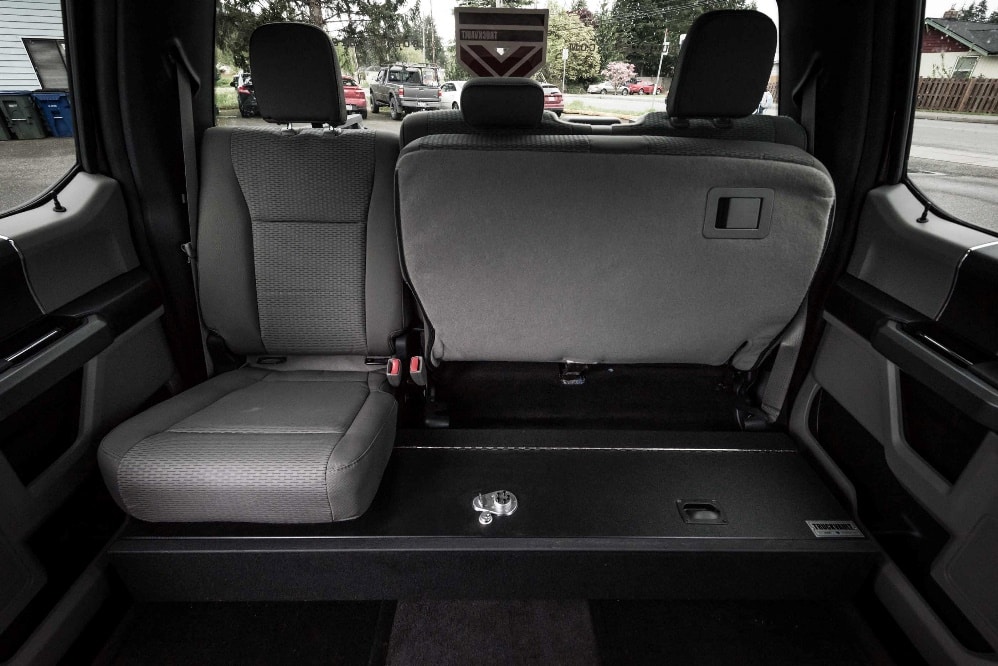

If you’re looking for a fully-concealed, full-size vault for the firearms in your truck, then this one’s for you. With six different finish options, you can customize the drawer faces to blend in or stand out. Other customizations include drawer divider configurations, carpet lining color, lock style, and one or two-door layouts.
Seat Back Gun Rack Sling
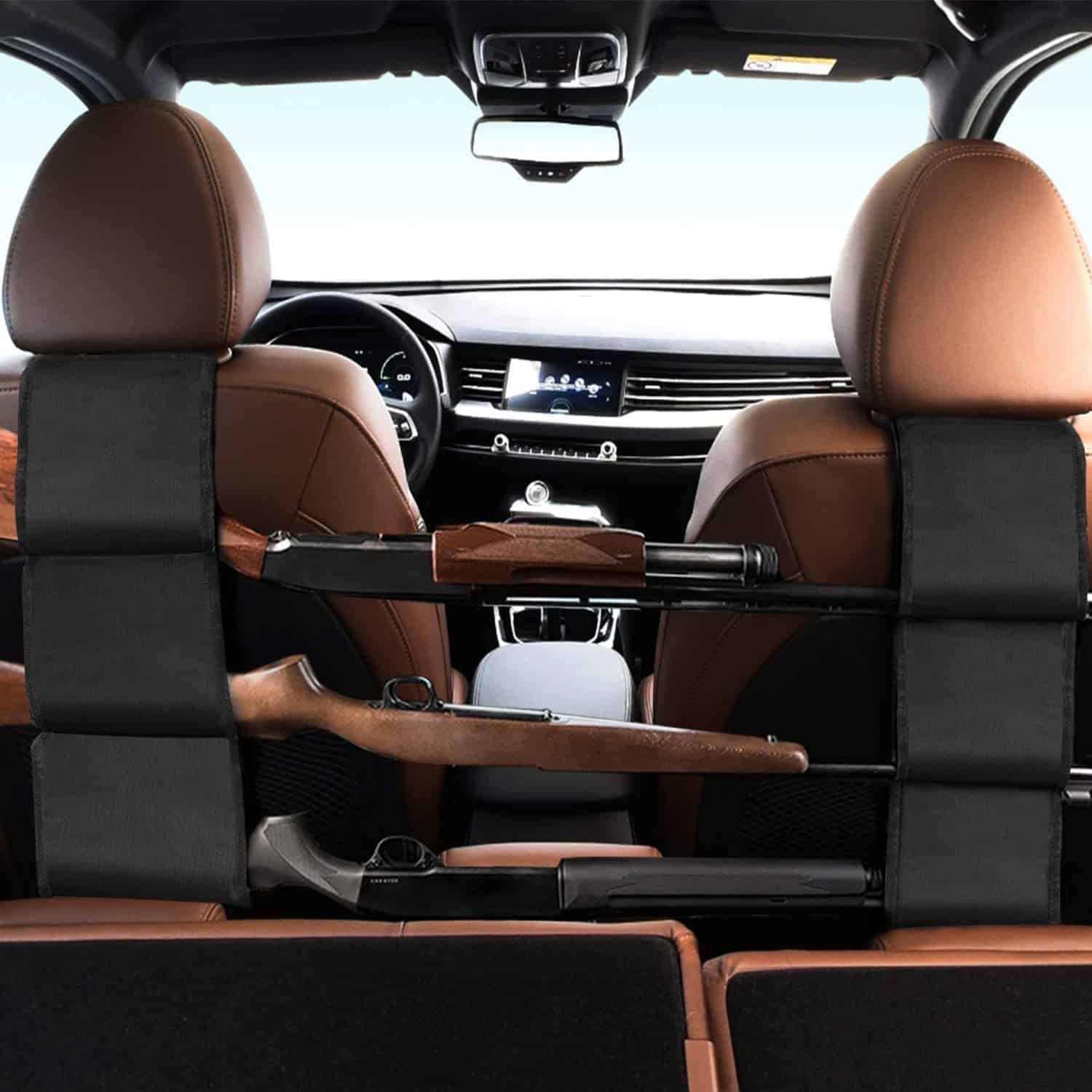

This sling is the durable firearm accessory organizer that every long gun owner needs. Made with high-quality 800D nylon, it should last you for years. It easily installs within minutes – all without destructive modifications to your interior. Simply buckle the top loop around your front headrests, then use the security cables at the bottom to attach it to your seat frame. When you’re not using it, it can easily be tucked away into your glove box or center console.
DARA Dash Mounted Handgun Holster
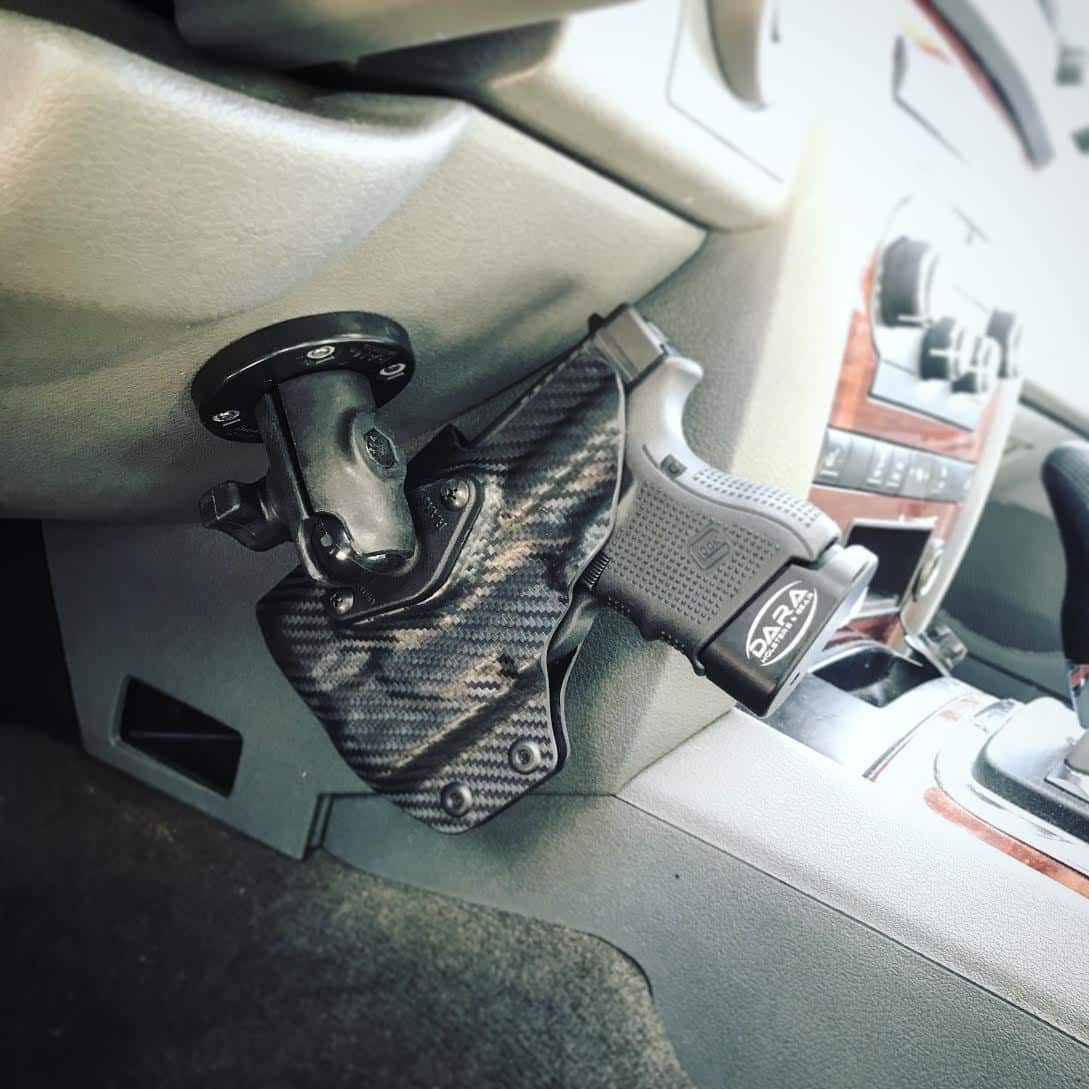

You can customize just about everything about this holder. Start by choosing your firearm model and your draw hand. You will also need to decide between left or right mounting side, depending on where you’re planning on placing it. It also comes in a handful of finish options – from black leather to carbon fiber, you can match it to your truck’s interior.
Which firearm accessory is your favorite? Whatever you choose, you can’t go wrong. If you’re a sucker for aftermarket accessories for your truck, then don’t overlook these options. Hopefully, this guide to the best tactical firearm pickup truck accessories of 2021 helped narrow down your choices.